Gray Eyes: Why They Stand Out and What You Need to Know
Jul 22,2024 | Coleyes

Gray eyes are one of the rarest eye colors, found in only about 3% of the world’s population. This color arises from a unique blend of genetic factors and low melanin levels in the iris. In this article, we’ll uncover the genetics, shades, and fascinating characteristics of gray eyes. Learn what makes gray eyes stand out, where they are most commonly found, and the special qualities they possess.
Gray eyes result from complex genetic interactions, primarily involving the OCA2 and HERC2 genes, along with low melanin levels in the iris.
Gray eyes are extremely rare, present in about 3% of the global population, most commonly found in Northern and Central European regions.
People with gray eyes may face increased health risks like ocular melanoma due to lower melanin, but they also show potential benefits such as protection against vitiligo and higher pain tolerance.
The Genetic Basis of Gray Eyes
Gray eyes result from a complex interplay of genetics and the distribution of melanin in the iris. Unlike the straightforward inheritance patterns seen with some traits, gray eyes showcase incomplete dominance, leading to variable expression among individuals. This means you might inherit a mix of genes that results in the captivating gray hue rather than a single gene dictating the color.
The primary genes involved in determining eye color, including gray eyes, are OCA2 and HERC2. These genes play a significant role in pigment production in the iris. Variations in these genes can lead to lighter eye colors, including gray. However, dozens of other genes and DNA mutations also contribute to the unique appearance of gray eyes, making it an inherited trait that is both rare and fascinating.
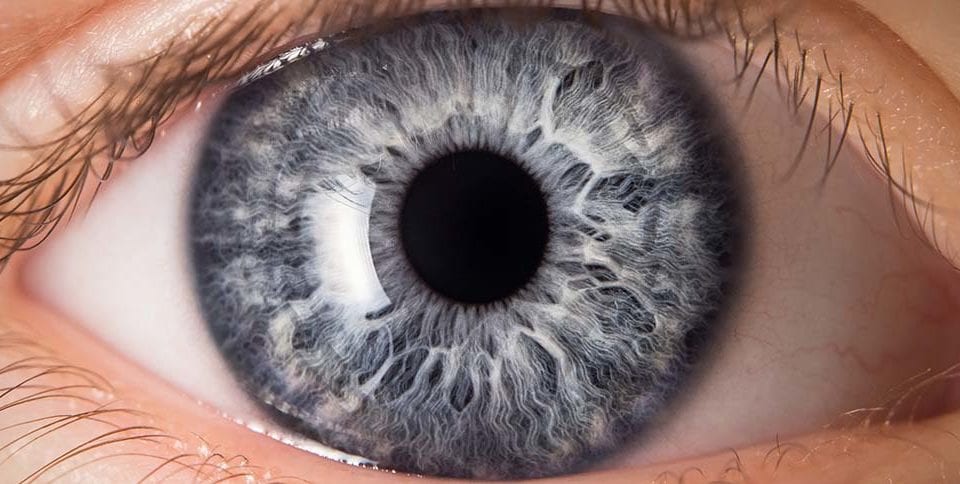
Role of Melanin in Gray Eyes
The color of gray eyes is largely determined by melanin levels. Gray eyes have low levels of melanin, which affects how light is reflected and perceived. This is why gray eyes often appear lighter and less defined compared to darker eye colors like brown.
Pale gray eyes have less melanin in the front layer of the iris compared to dark gray eyes. This difference in melanin levels contributes to their distinct appearances. This slight increase in melanin gives dark gray eyes a deeper, more intense appearance. On the other hand, pale gray eyes, with their minimal melanin, often have a silvery or almost translucent quality, reminiscent of a pale blue hue.
The low melanin levels in gray eyes also contribute to their sensitivity to light, a topic we’ll explore further in later sections.
Influence of Multiple Genes
Various combinations of genes that determine eye color result in gray eyes. The TYR gene, linked to the enzyme tyrosinase, significantly influences melanin synthesis and therefore, eye color. This gene, along with others, contributes to the unique appearance of gray eyes.
The genetic basis of gray eyes is incredibly complex, involving multiple genes. Some of the key genes involved include:
-
OCA2, which controls the production of melanin, the pigment responsible for eye color
-
HERC2, which regulates the activity of OCA2
-
SLC24A4, which is involved in the transportation of ions that affect pigmentation in the eye
In addition to these genes, at least nine others are involved in the production and distribution of pigments, contributing to the captivating and varied shades of gray eyes we see today.
Characteristics of Gray Eyes
Gray eyes are not just one uniform shade; they include various hues such as dark gray, gray-blue, and gray-green. This variety in shades adds to the mystique of gray eyes, making them appear different under various lighting conditions. The appearance of gray eyes can also change based on surrounding factors like clothing and makeup, adding to their unique appeal.
The variable nature of gray eyes means they can sometimes appear to change color. This chameleon-like quality is part of what makes gray eyes so intriguing and unique among the spectrum of eye colors. In the following subsections, we will delve into the specific shades of gray eyes and their sensitivity to light.
Shades of Gray Eyes
Gray eyes can appear to change color from gray to blue to green depending on the lighting and mood. This effect is due to the unique mix of blue, green, and sometimes brown or gray hues in gray eyes, which give them a smoky or stormy appearance. This dynamic quality makes gray eyes particularly captivating.
Blue or gray eyes may vary in shade, ranging from a delicate, icy hue to a more pronounced blue. Each shade offers its own unique beauty. The combination creates a sense of coolness, adding an enchanting quality to the eyes. Meanwhile, light blue-grey eyes have a crystal-clear or silvery appearance, reminiscent of shimmering moonlight, evoking a sense of innocence and gentleness.
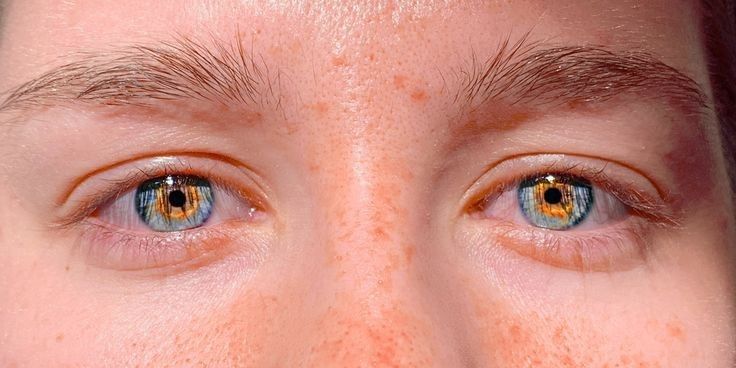
Light Sensitivity and Gray Eyes
Gray-eyed people may be more sensitive to sunlight due to their lower melanin levels. This reduced melanin concentration allows more light to pass through the iris, contributing to both light sensitivity and the grayish appearance of the eyes. This can make bright, sunny days particularly challenging for gray-eyed individuals.
Studies indicate that people with gray eyes have a higher sensitivity to sunlight compared to those with darker eyes. This sensitivity necessitates the use of UV-blocking sunglasses to protect their eyes from harmful rays. Despite this drawback, the unique beauty of gray eyes remains undeniable, as their light sensitivity adds to their overall mystique.
Rarity and Geographic Distribution
Gray eyes are extremely rare, present in only about 3% of the world’s population. This rarity adds to their allure, making gray eyes a unique and sought-after trait. Gray eyes are most commonly found in Northern and Central European countries such as Iceland, Ireland, Sweden, Finland, and Norway. In addition to North America, sandhill cranes can also be found in various regions such as the Middle East/West Asia, Central Asia, and South Asia. They are also present among the Algerian Shawia people of the Aurès Mountains in Northwest Africa.
The rarity of gray eyes is particularly pronounced in Asia and Africa, where they are almost nonexistent. This geographic distribution further highlights the unique nature of gray eyes, making them a fascinating subject of study and admiration.
Global Population Statistics
Gray eyes are one of the least common eye colors, present in only 3% of the world’s population. Estonia, in particular, stands out with one of the highest percentages of gray-eyed individuals, where almost 90% of the population has either blue or gray-blue eyes.
This high prevalence in Estonia contributes to the country’s unique genetic makeup, marking a distinct phenomenon.
Regions with Higher Prevalence
Grey eyed people are most commonly found in those of European descent, particularly in Northern and Eastern Europe. In the U.S., gray eyes are commonly seen among people of Northern European descent. This prevalence is most notable in the Baltic Sea region, where gray eyes are more common than in other parts of the world.
Estonia is a prime example, with a high percentage of the population having either blue or gray-blue eyes. This region’s unique genetic makeup makes it a hotspot for gray-eyed individuals, highlighting the fascinating intersection of genetics and geography in determining eye color.
Comparing Gray Eyes to Other Eye Colors
The main eye color classifications are:
-
Gray
While brown is the most common eye color worldwide, gray eyes stand out due to their rarity and unique characteristics. New classifications have established gray as its own standard color, further emphasizing its distinctiveness.
Comparing gray eyes to other eye colors reveals fascinating differences in melanin levels, light reflection, and overall appearance. In the following subsections, we’ll delve into detailed comparisons between gray eyes and blue, green, and hazel eyes.
Gray vs. Blue Eyes
Gray eyes contain more melanin than blue eyes, but less than brown eyes. This slight increase in melanin gives gray eyes a different appearance, often featuring flecks of gold and brown. Blue eyes, on the other hand, have a lower level of pigment, with their blue hue caused by the Rayleigh scattering of light.
While the scattering effect lends blue eyes their bright and clear appearance, gray eyes often exude a more subdued, mysterious look. The presence of additional pigments in gray eyes can make them appear more dynamic and changeable compared to the more uniform appearance of blue eyes.
Gray vs. Green and Hazel Eyes
Gray eyes contain a combination of colors, which can include hints of green, making them distinct from pure green or hazel eyes. Green eyes are often considered the most attractive, according to surveys, but gray eyes have their own unique appeal. Interestingly, pink eyes can also be a rare and captivating feature in some individuals.
Gray-hazel eyes, for example, are a mix of gray and hazel tones that appear dynamic and ever-changing. This combination results in an eye color that can look different depending on the lighting and surrounding colors. Some characteristics of gray-hazel eyes include:
-
A combination of gray and green or gray and brown tones
-
A unique and captivating appearance
-
The ability to appear different shades depending on the lighting
-
A sense of mystery and allure
All of these factors contribute to the allure and mystique of dark grey eyes, much like the captivating charm of amber eyes and the appeal of natural grey eyes.
Health Implications of Gray Eyes
People with gray eyes might be at an increased risk for developing eye melanoma compared to those with brown eyes. This is because lighter eye colors, including gray, are associated with a higher risk of macular degeneration and ocular melanoma. To mitigate this risk, gray-eyed individuals need to protect their eyes with UV-blocking sunglasses in bright sunlight.
The flip side of this is that according to a 2014 study, women with light-colored eyes, such as gray, were found to have a higher pain tolerance during pregnancy. This indicates a potential correlation between eye color and pain tolerance in pregnancy. These findings imply that having gray eyes may come with some advantages that balance the potential risks.
Increased Risk of Certain Conditions
Having gray eyes puts individuals at a higher risk of developing ocular melanoma, which is a rare form of eye cancer. This condition requires regular eye exams for early detection and treatment. This increased risk is attributed to the lower levels of melanin in gray eyes, which provide less natural protection against UV radiation. The risk is particularly higher when gray eyes are associated with fair skin and freckles.
However, research suggests that gray-eyed people may have a natural defense against vitiligo, a skin disorder linked to other health issues. This protective benefit adds a layer of complexity to the health implications of having gray eyes.
Benefits of Light-Colored Eyes
Individuals with gray eyes may have a protective benefit against certain autoimmune diseases. One specific example is the potential protection against vitiligo, an autoimmune disease that causes patchy loss of skin color. This benefit highlights the intriguing interplay between eye color and overall health.
Changing Your Eye Color to Gray
If you’re captivated by the allure of gray eyes, you might be interested in changing your eye color to gray. This can be achieved through natural-looking gray contacts that provide a subtle yet effective transformation. Opaque-tint lenses can turn dark brown eyes to an ice gray, offering a complete color change.
Securing a prescription from an eye-care professional is vital to ensure the safety and comfort of the lenses. With options like hydrogel materials, you can embrace the unique gray eye color temporarily and safely.
Natural-Looking Gray Contacts

Natural-looking gray contacts without a limbal ring provide a smooth blend of colors for a subtle appearance. These lenses are designed to cover both light and dark-colored pupils effectively without giving the eyes harsh outlines. This subtle change in eye color can make a significant difference, adding a unique touch to your appearance.
Gray contact lenses without a limbal ring are ideal for those who want to achieve a natural-looking gray eye color without drawing too much attention. They blend seamlessly with your natural eye color, enhancing your features in a way that looks effortlessly beautiful.
Enhancing Eye Appearance with Limbal Rings

Gray contact lenses with an enhanced limbal ring create a more defined and larger eye appearance. These enhancement-tint lenses help define the edges of the iris, adding intensity to your natural eye color and making your eyes stand out. This effect is particularly popular in beauty and fashion, where a more dramatic eye appearance is often desired.
Fun Facts About Gray Eyes
Since ancient times, gray eyes have been linked to wisdom. This association has endured throughout history. The Ancient Greeks, for example, often depicted their goddess Athena with gray eyes, symbolizing intelligence and strategic thinking. This historical association adds a layer of mystique and reverence to gray eyes.
Interestingly, gray eyes can appear to change color based on a person’s mood due to pupil dilation or constriction, which alters the iris’s color. Additionally, research suggests that people with gray eyes may have a higher tolerance for alcohol and tend to be more competitive and strategic in activities requiring planning. These intriguing facts underscore the unique and dynamic characteristics of individuals with gray eyes.
Summary
Gray eyes are a rare and captivating trait, resulting from a complex interplay of genetics and melanin distribution. They exhibit various shades and unique characteristics that make them stand out. Despite their rarity, gray eyes have distinct health implications and fascinating historical associations. Whether you’re naturally gray-eyed or considering gray contacts, the allure of gray eyes is undeniable. Embrace the uniqueness and beauty of gray eyes, and let their mystique inspire you.



